About heart disease
Some heart attacks are sudden and intense. But most
start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. It’s important not to ignore the symptoms you are having.
Here are some of the signs that can mean a heart attack is happening:
- Chest discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes, or that goes away and comes back. It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain.
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. Symptoms can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath. May occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea or lightheadedness.
- With women, the most common heart attack symptom is chest pain or discomfort. But women are more likely than men to have some of the other common symptoms, particularly shortness of breath, nausea/vomiting, and back or jaw pain.
- Face Drooping
- Arm Weakness
- Slurred Speech
If you exhibit any of the 3-signs above, it’s time to Call 9-1-1! Immediately!
- Call 9-1-1 even if you’re not sure it’s a heart attack – call immediately.
2. Contact your local emergency medical services (EMS) such as the fire department or ambulance.
3. EMS staff can begin treatment when they arrive — up to an hour sooner than if someone gets to the hospital by car.
4. Patients with chest pain who arrive by ambulance usually receive faster treatment at the hospital.
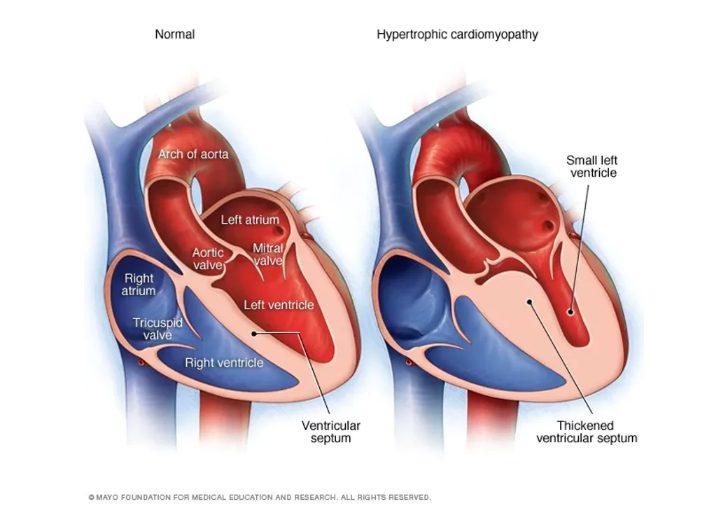
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a disease in which the heart muscle (myocardium) becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied). The thickened heart muscle can make it harder for the heart to pump blood
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy often goes undiagnosed because many people with the disease have few, if any, symptoms and can lead normal lives with no significant problems. However, in a small number of people with HCM, the thickened heart muscle can cause shortness of breath, chest pain or problems in the heart’s electrical system, resulting in life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
.